52 lines
1.5 KiB
Markdown
52 lines
1.5 KiB
Markdown
---
|
|
title: Flume
|
|
updated: 2022-05-24 18:29:31Z
|
|
created: 2021-05-04 14:58:11Z
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
# Apache Flume
|
|
|
|
Streaming data into cluster
|
|
Developed with Hadoop in mind
|
|
|
|
- Build-in sinks fir HDFS and Hbase
|
|
- Originally made to handle log aggregation
|
|
|
|
***Flume is buffering data before delivering to the cluster.***
|
|
|
|
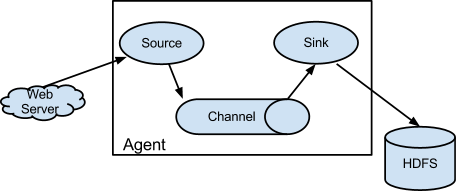
## Anatomy of a Flume Agent and Flow
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Three components of a Flume Agent:
|
|
|
|
- Source
|
|
- Where data is comming from
|
|
- Optionally Channel Selectors and Interceptors
|
|
- Selectors:
|
|
- based on some selection the data is sent somewhere
|
|
- Interceptors:
|
|
- Data can add or reschape the data
|
|
- Channel
|
|
- how the data is transferred between Source and Sink (via memory or files)
|
|
- Sink
|
|
- Where the data is going
|
|
- multiple Sinks and can be organized into Sink Groups
|
|
- A Sink can connect to only ***one*** Channel
|
|
- Channel is notified te delete a message once the Sink processes it
|
|
|
|
### Build-in Source Types:
|
|
|
|
- Spooling directory, Avro (specific Hadoop format), Kafka, Exec (command-line), Thrift, Netcat (tcp/ip), HTTP, Custom, etc
|
|
|
|
### Build-in Sink Types:
|
|
|
|
- HDFS, Hive, HBase, Avro, Thrift, Elasticsearch, Kafka,Custom
|
|
|
|
Flume Example
|
|

|
|
|
|
First layer close to source and proces data. ie are in a local datacenter.
|
|
The second layer collects from and incests into the sink.
|
|
Between first amnd second layer of agents are source AVRO and Sink AVRO to transfer data very efficient.
|